Understanding Four-Wheel Drive and All-Wheel Drive
When it comes to choosing a vehicle, one of the important factors to consider is the drivetrain. Two popular options that often come up in discussions are four-wheel drive (4WD) and all-wheel drive (AWD). While both drivetrains offer improved traction and control, there are some key differences between the two. In this article, we will explore these differences to help you make an informed decision.
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD)

Four-wheel drive, also known as 4WD or 4×4, is a drivetrain system that distributes power to all four wheels of a vehicle. It is commonly found in trucks, SUVs, and off-road vehicles. The main purpose of 4WD is to provide maximum traction and control in off-road or challenging terrains.
4WD systems typically have a transfer case that allows the driver to switch between two modes: 2WD (two-wheel drive) and 4WD. In 2WD mode, power is sent only to either the front wheels or the rear wheels, depending on the vehicle’s configuration. This mode is suitable for regular driving conditions on paved roads, where extra traction is not required.
On the other hand, when the 4WD mode is engaged, power is distributed to all four wheels simultaneously. This mode is ideal for off-road adventures, snowy conditions, and other situations where additional traction is needed. By sending power to all wheels, 4WD helps the vehicle navigate through challenging terrain, such as mud, rocks, or steep inclines.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
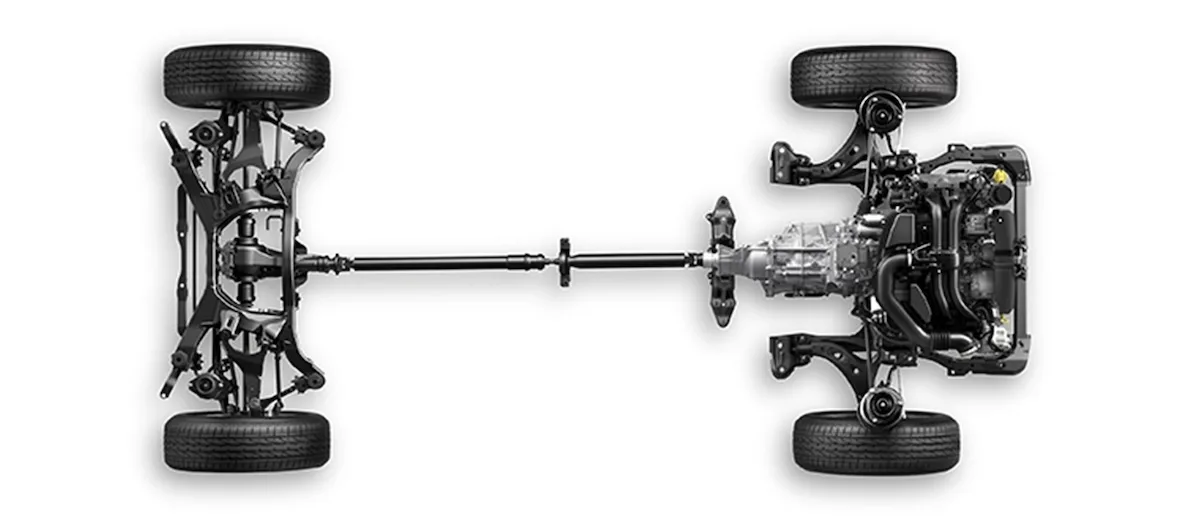

All-wheel drive, commonly referred to as AWD, is a drivetrain system that continuously sends power to all four wheels of a vehicle. Unlike 4WD, AWD is not typically designed for off-road adventures but rather for improved handling and performance on various road conditions.
AWD systems are more commonly found in sedans, crossover SUVs, and some sports cars. The main advantage of AWD is that it provides better traction and stability on wet or slippery roads, making it a popular choice for those who frequently drive in adverse weather conditions.
Unlike 4WD, most AWD systems are always active and do not require any input from the driver. They continuously monitor the road conditions and distribute power to the wheels with the most grip. This automatic power distribution helps enhance the vehicle’s stability and handling, especially when cornering or accelerating on uneven surfaces.
Key Differences
Now that we have a basic understanding of 4WD and AWD, let’s delve into the key differences between the two:
Intended Use:
4WD is primarily designed for off-road use and is commonly found in vehicles built for rugged terrains. It provides maximum traction and control in challenging conditions, making it ideal for adventurers and off-road enthusiasts. On the other hand, AWD is more focused on enhancing on-road performance and handling, providing better stability and control in various weather conditions.
Engagement:
In most 4WD systems, the driver has the ability to manually engage or disengage the 4WD mode as needed. This allows them to switch between 2WD and 4WD modes depending on the driving conditions. AWD systems, on the other hand, are typically always active and do not require any input from the driver. They continuously monitor the road conditions and adjust power distribution accordingly.
Complexity:
4WD systems tend to be more complex and robust compared to AWD systems. They often include additional components such as a transfer case, locking differentials, and low-range gearing. AWD systems, on the other hand, are generally simpler and lighter, as they do not require the same level of off-road capabilities.
Fuel Efficiency:
Due to their additional components and the ability to engage or disengage the 4WD mode, 4WD vehicles often have lower fuel efficiency compared to AWD vehicles. AWD systems, being always active and continuously adjusting power distribution, can provide better fuel efficiency in regular driving conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between four-wheel drive (4WD) and all-wheel drive (AWD) ultimately depends on your specific needs and driving conditions. If you frequently find yourself off-road or in challenging terrains, 4WD might be the better option for you. On the other hand, if you prioritize enhanced on-road performance and better handling in adverse weather conditions, AWD might be the more suitable choice.
Remember to consider factors such as intended use, engagement, complexity, and fuel efficiency when making your decision. Ultimately, both drivetrains offer their own set of advantages and can greatly enhance your driving experience based on your unique requirements.